A strait is a navigable waterway connecting two bigger our bodies of water. It is a pure formation and is commonly slender. Some straits additionally act as maritime chokepoints and are key to persevering with easy maritime commerce worldwide. Some examples embrace the Hormuz Strait, the Strait of Malacca, and so on.
Straits not solely cut back transit instances and prices by offering the quickest sea routes between two locations, however they’re additionally geopolitically essential. Civilisations prior to now strove to ascertain their dominance on these strategic waterways, which meant controlling important commerce routes of the respective area.
Even immediately, straits are thought of extraordinarily essential for the free circulation of commerce, commerce, concepts and folks globally.
In this text, we’ll talk about the 15 longest straits on the planet. So, let’s start!
1. Strait of Malacca
The Strait of Malacca is alleged to be the longest strait. It is 800 km or 500 miles lengthy and 65-250 km broad and connects the Indian and Pacific Oceans by way of the Andaman and South China Sea. It is known as after the Malacca Sultanate that dominated modern-day Malacca, Malaysia, between 1400-1511.
As the first delivery channel between two main oceans, the strait has nice financial and strategic significance, connecting main Asian economies.
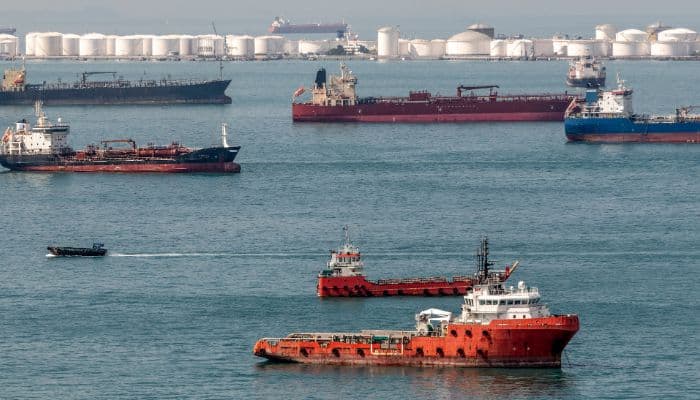

It can also be part of the Maritime Silk Road that goes from the coast of China to India’s southern tip to Mombasa. From right here, it runs to the Red Sea via the Suez Canal to the Mediterranean, Upper Adriatic area, Trieste and from there to Central Europe and the North Sea via rail connections.
More than 95,000 ships go via it yearly, making it a busy waterway, delivery about 25% of all traded objects like oil, Chinese manufactured items, Indonesian espresso and 1 / 4 of all international oil coming from the Persian Gulf to the markets in Asia.
2. Bass Strait
The Bass Strait distinguished Tasmania from mainland Australia whereas providing a sea route between the Great Australian Bight and the Tasman Sea, making it a significant maritime path to Port Philip Bay.
Per analysis, the Bay was shaped because of rising sea ranges on the finish of the final glacial interval. It has been named after George Bass, an English doctor and explorer.
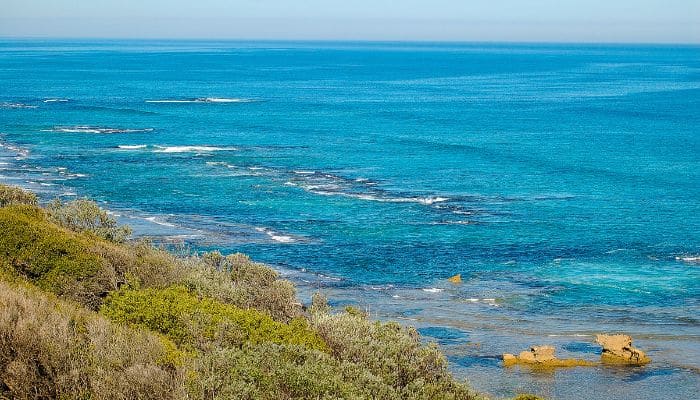

Bass Strait is round 500 km lengthy, 250 km large, and 60 m deep. Its widest level is 350 km, between Cape Portland on the northeastern finish of Tasmania and Point Hicks on mainland Australia.
Over 100 islands lie within the Bass Strait, with many oil and pure fuel fields, such because the Halibut and the Kingfish fields, found between 1960-1980.
3. Davis Strait
Lying between Baffin Island and Greenland, this strait is an entry level to Baffin Bay. It is a large stretch of water over 950 km throughout its best width and is roughly 300 km large. Its underwater topography includes a ridge shaped 45-62 million years in the past, extending from the Baffin island coast to Greenland. Along this ridge are discovered the Strait’s shallowest waters.
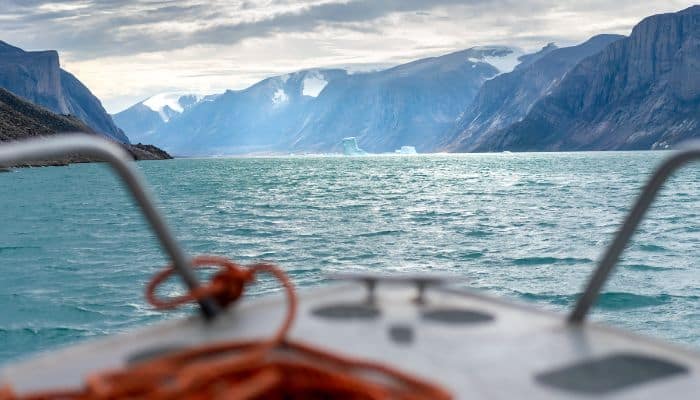

It is also called the northern arm of the Atlantic Ocean north of the Labrador Sea. The Davis Strait was first explored by John Davis, an English explorer and chief of three expeditions organised by Merchants of London, England, in 1585-87. By the 1650s, the area had develop into a preferred spot for whale looking.
Another attribute function of the Davis Strait is its ruthless tides, which will be as excessive as 30 to 60 ft. Per the Geological Survey estimates, the area across the Strait holds as much as 13% of the worldwide undiscovered oil deposits and 30% of untapped fuel reserves.
4. Denmark Strait
Also known as the Greenland Strait, this waterway lies between Greenland to its northwest aspect and Iceland to its southeast. To its northeast lies Jan Mayen, a Norwegian island.

It hyperlinks the Greenland Sea, a part of the Arctic Ocean, to the Irminger Sea, part of the Atlantic Ocean. The world’s greatest underwater waterfall, the Denmark Strait Cataract’ is situated on the western aspect of the Denmark Strait.
The chilly East Greenland Current within the strait takes icebergs to the North Atlantic. The Denmark Strait is wealthy in fisheries, too. It is 480 km lengthy and 290 km large at its narrowest level between Straumnes and Cape Tupinier.
5. Korea Strait
This strategic strait in East Asia lies between Japan and Korea, linking the East China Sea, the Yellow Sea and the Sea of Japan. To its northern aspect, the Korea Strait is surrounded by the Korean Peninsula’s southern coast. To its south lie the Japanese islands of Kyushu and Honshu.
It is a crucial commerce route; many delivery lanes go via it, with Korea and Japan permitting free passage via the waterway. It can also be the location of the Battle of Korea throughout the Korean War.

The strait is about 200 km large with a mean depth of 90 to 100 m. Passenger Ferries ply within the strait operating from Busan and Geoje in South Korea to the Japanese ports of Tsushima, Hiroshima and Shimonoseki.
6. Torres Strait
Torres Strait is between Australia and New Guinea, providing a passage between the Coral Sea on the east and the Arafura Sea within the western Pacific Ocean. It is 130 km large and has a number of reefs and shoals, making navigation within the strait fairly harmful.
It was found in 1606 by a mariner referred to as Luis Vaez de Torres, and the existence of this waterway was stored a secret till 1764. Captain James Cook was the second European to cross the strait in 1774.

Several Torres Strait Islands have a historical past of human habitation courting again to 2500 years. These communities have distinct cultures and traditions.
In the strait are about 580 coral reefs, just like the Eastern Patch reefs and Warrior Reefs, that span 2400 km2 of space. It additionally has one of the crucial intensive seagrass beds throughout the globe.
7. Bering Strait
Towards the north, the Bering Sea meets the Arctic Ocean by way of the Bering Strait at its narrowest level. It separates Russia and Alaska on the closest level, 53 miles or 85 km.

The Strait is comparatively shallow, with a mean depth of fifty m and solely 90 m deep at its deepest level. Per a number of theories, this strait was as soon as a land bridge between North America and Asia throughout the Ice Age. During these instances, sea ranges fell and shaped a land bridge, permitting vegetation and animals of the area to unfold far and large.
Bering Strait has many islands, such because the Diomede and St Lawrence Islands. Storms are frequent on this area in winter, and many of the Bering Sea stays coated with ice, which steadily melts and drifts into the strait as summer time knocks.
8. Yucatan Channel or Straits of Yucatan
Also referred to as the Straits of Yucatan, this waterway between Mexico and Cuba hyperlinks the Yucatan Basin within the Caribbean with the Gulf of Mexico.
As the strait’s water enters the Gulf of Mexico, it passes via a shallow space referred to as Campeche Bank. This area is residence to quite a few coral reefs. Many reef-building corals are discovered right here, reminiscent of Acropora palmate and others.

Several corals died within the Nineteen Nineties; nevertheless, recolonisation is steadily occurring. Campeche Bank is sort of various, just like different areas of the Yucatan Channel, wealthy in fisheries.
This channel is greater than 200 km or 120 miles large and round 2800 m or 9200 ft deep close to the Cuban coast, its deepest level. This area is overexploited and suffers from the ils of air pollution.
9. Bosphorus Strait
Bosphorus Strait is a major seaway connecting the Black Sea to the Marmara, Aegean, and Mediterranean Sea via the Dardanelles. It additionally joins many water our bodies alongside the japanese Mediterranean, the Near East, the Balkans, and Western Eurasia.
Hence, it connects the Black Sea to the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean via Gibraltar and the Indian Ocean by way of the Suez Canal. It is an important sea passage, particularly for commodities coming from Russia.
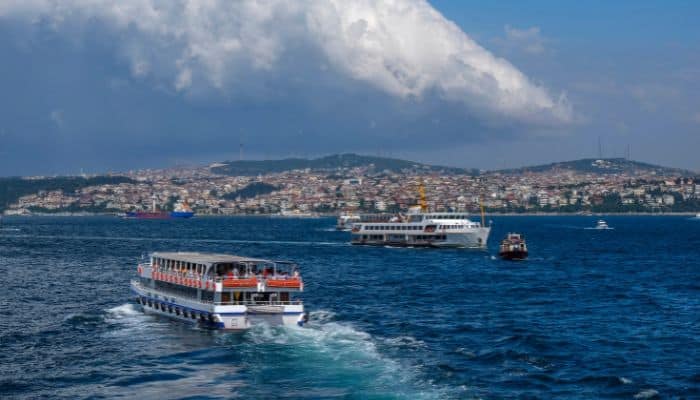

It is 31 km or 19 miles lengthy, 700 m large and 110 m deep. This strait kinds part of the border dividing Asian and European continents. It additionally divides Turkey by separating Anatolia from Thrace. It can also be the narrowest strait on the planet used for navigation internationally.
The coasts of Bosphorus are closely populated. The metropolitan inhabitants of Istanbul, comprising round 17 million folks, extends inward from each banks. Also, the Bosphorus Strait, together with the Dardanelles Strait, is known as the Turkish Straits.
10. Tartary Strait
The Strait of Tartary within the Pacific Ocean divides Sakhalin Island, Russia, from the Asian mainland. This 632 km lengthy strait connects the Sea of Okhotsk and the Sea of Japan. The northern a part of Tartary Strait referred to as the Amur Liman, will get freshwater from the Amur River.

The strait is 7 to 342 km large and fewer than 210 m deep. Its coasts are dotted with many Russian ports and harbours like Lesogorsk, Uglegorsk and Sovetskaya Gavan. Operations at these services are restricted by thick ice from November to May.
In 1956, the Soviet Government proposed the development of a causeway over this strait to stop chilly water from getting into the Sea of Japan, thereby elevating the temperatures across the latter.
11. Luzon Strait
The Luzon Strait lies between Luzon and Taiwan. This 250 km large waterway is residence to the most important ocean waves on the planet. These mighty waves will be greater than 170 m in peak and are primarily seen within the northern a part of the Luzon Strait.
However, these waves or currents hardly ever break the floor, therefore pose no hazard to delivery, however are seldom captured by satellites.

Luzon Strait hyperlinks the Philippine Sea with the South China Sea within the western Pacific Ocean. It is a crucial seaway for maritime commerce as a number of ships from the Americas cross it to succeed in East Asian ports.
Also, submarine cables go via this strait, offering entry to information and telephony providers to China, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan and Hong Kong.
12. Palk Strait
The Palk Strait is between the Indian State of Tamil Nadu and the Jaffna District of the Northern Province of Sri Lanka, linking the Bay of Bengal with Palk Bay.
This waterway connecting India and Sri Lanka has been named after the Governor of Madras, Robert Palk, who served throughout the Company Raj within the 1700s.

The Palk Strait is lower than 9.1 m deep and is 64 to 137 km large. Many rivers circulation into the strait, such because the Vaigai River. A placing function of the strait is its waves, which differ throughout the north and south. To the north, the waves are normally swell waves, and to the south, in Palk Bay, are normally sea waves.
At the southern finish of Palk Bay lies a sequence of islands and reefs, collectively referred to as the Ram Setu or Bridge of Ram, in Hindu mythology.
13. Sunda Strait
Sunda Strait lies between Java and Sumatra in Indonesia, linking the Java Sea with the Indian Ocean. The Sunda Strait is a triangular formation with 2 bays to its north.
It extends in a southwest-to-northeast trend, with a width of 24 km between Cape Tua and Java’s Cape Pujat. The strait is sort of broad and deep on the southwestern aspect and narrows all the way down to the northeast, turning into shallow, with a 20 m depth.

Apart from its shallowness, it has robust tidal currents and man-made obstructions like oil platforms and sandbanks, making navigating harmful. Most ships now use Malacca Strait as an alternative of this waterway.
The waterway derives its identify from the Sunda Kingdom, which managed Java’s western half from 669-1579. It can also be mentioned that this identify alludes to the Sudanese populations indigenous to West Java.
It was a significant delivery route, and the Dutch East India Company used it to succeed in the Indonesian Spice Islands.
14. Strait of Gibraltar
The Strait of Gibraltar hyperlinks the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea, separating Europe and Africa by 13 km of ocean at its narrowest level, mendacity between Point Marroqui in Spain and Point Cires in Morocco.
The strait derives its identify from the Rock of Gibraltar. It can also be referred to as Bab al-maghrib in Arabic, which means ‘the Gate of the West’ or ‘Gate of Sunset’.

BirdLife International recognized it as an Important Bird Area because of hundreds of seabirds flying throughout it emigrate between the Mediterranean and the Atlantic. Some birds embrace Scopoli and Balearic shearwaters, razorbills, Atlantic puffins, and so on.
Also, an orca pod, one of many few inhabiting Western European waters, lives across the Strait of Gibraltar.
The Strait of Gibraltar additionally serves as a vital delivery route from the Mediterranean to the Atlantic. Ferries carry folks throughout the strait between Spain and Morocco, Spain and Ceuta, and Gibraltar to Tangier.
15. Cook Strait
Cook Strait hyperlinks the Tasman Sea with the South Pacific Ocean and separates the North and South Islands of New Zealand.
Named after James Cook, the primary European who sailed via the waterway in 1770, this 22 km large strait is thought for its harmful and unpredictable waters.

It finds point out in numerous Maori tales. In one of many tales, Hine Poupou has been described as the primary girl to cross this strait with the assistance of a dolphin.
Given the robust tidal flows right here, this area can also be mentioned to be a doubtlessly wealthy supply of tidal vitality.
Regarding navigation, ferry providers within the strait run between Picton in Marlborough Sounds and Wellington. Cook Strait additionally helps many cetacean species, together with bottlenose, frequent and dusky dolphins, killer whales, sperm whales, sei and southern proper whales, big squids, fur seals, and so on.
You may also prefer to read-
- 10 Major Straits Of Asia
- 10 Best Great Lakes Ship Tracker Tools
- 10 Gulf of Martaban Facts You Might Not Know
- 12 Gulf Of Mannar Facts You Might Not Know
- 10 Celtic Sea Facts You Should Know
- 9 Interesting West Philippine Sea Facts You Must Know
- 13 Gulf Of Riga Facts You Must Know
Disclaimer: The authors’ views expressed on this article don’t essentially mirror the views of Marine-Salvage. Data and charts, if used within the article, have been sourced from obtainable data and haven’t been authenticated by any statutory authority. The creator and Marine-Salvage don’t declare it to be correct nor settle for any accountability for a similar. The views represent solely the opinions and don’t represent any pointers or suggestions on any plan of action to be adopted by the reader.
The article or photographs can’t be reproduced, copied, shared or utilized in any kind with out the permission of the creator and Marine-Salvage.
Do you may have data to share with us ? Suggest a correction
Latest Maritime Knowledge You Would Like:

5 Major Ports In Cuba

10 Important Canals In The United States

10 Titanic Captain Facts You Might Not Know
What is Lowest Astronomical Tide?

10 Timor Sea Facts You Might Not Know

8 Interesting Facts About Cape Cornwall

About Author
Zahra is an alumna of Miranda House, University of Delhi. She is an avid author, possessing immaculate analysis and enhancing expertise. Author of a number of tutorial papers, she has additionally labored as a contract author, producing many technical, inventive and advertising and marketing items. A real aesthete at coronary heart, she loves books somewhat greater than anything.
Get the Latest Maritime News Delivered to Your Inbox!
Our free, quick, and enjoyable publication on the worldwide maritime trade, delivered on a regular basis.














