The maritime trade’s most essential issues are the security of personnel and prevention of marine air pollution for clean cargo transportation and marine operation at excessive seas. To obtain this, the International Maritime Organization (IMO) depends on its two very robust pillars: SOLAS & MARPOL – The International Conventions for safeguarding human life and marine surroundings from all types of pollutions and accidents.
Read: MARPOL – The Ultimate Guide
What is SOLAS Convention?
The phrase SOLAS is an abbreviation and SOLAS full type is “Safety Of Life At Sea”, a world maritime treaty, often known as SOLAS Convention or International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS), which establishes the least security measures within the building, gear and operation of service provider ships.
IMO SOLAS 74, the final adopted revised conference of 1974, contains quite a few rules beneath completely different SOLAS chapters, which offers with security precautions and security procedures ranging from the development of the ship to actual emergency like – “Abandon Ship”. The conference is up to date to fulfill the security norms within the fashionable delivery trade on occasion.
This article explains the contents of SOLAS chapters and rules offering a abstract of SOLAS, i.e. completely different chapters of SOLAS and the rules they carry. Marine-Salvage has supplied hyperlinks of assorted articles which can assist the readers to grasp how the regulation of the SOLAS Annexes is carried out on a seagoing vessel and the significance of SOLAS.
SOLAS 74
SOLAS CONTENT:
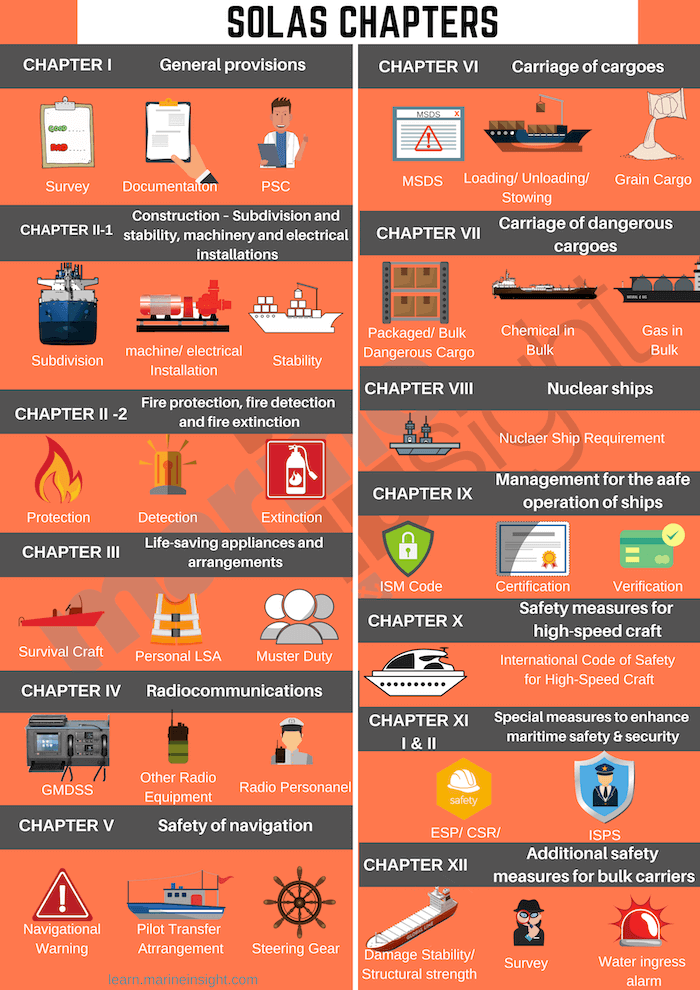
The SOLAS 1974 worldwide maritime treaty contains of 13 chapters and every chapter has its personal set of rules. The Following are the checklist of SOLAS all 14 chapters and the rules they comprise:

The International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS), 1974 describes the requirement for all service provider ship of any flag state to adjust to the minimal security norms laid down within the chapters that are as follows:
Chapter I – General Provisions: Surveys and certification of all the security objects and so on are included.
Chapter II-1 – Construction – Subdivision and stability, equipment and electrical installations: Deals with watertight integrity of the ship, particularly for passenger vessel.
Chapter II-2 – Fire safety, fireplace detection and fireplace extinction: This chapter elaborates the means and measure for fireplace safety in lodging, cargo areas and engine room for the passenger, cargo and tanker ship.
Chapter III – Life-saving home equipment and preparations: All the life-saving home equipment and there use in several conditions is described.
Chapter IV – Radio communications: Includes necessities of GMDSS, SART, EPIRB and so on for cargo and passenger vessel.
Chapter V – Safety of navigation: This chapter offers with all of the seagoing vessels of all sizes, from boats to VLCCs, and contains passage planning, navigation, misery sign and so on.
Chapter VI – Carriage of Cargoes: This chapter defines storage and securing of various kinds of cargo and containers, however doesn’t embrace oil and fuel cargo.
Chapter VII – Carriage of harmful items: Defines the International Maritime Goods Code for storage and transportation of harmful items.
Chapter VIII – Nuclear ships: The code of security for a nuclear-propelled ship is said on this chapter.
Chapter IX – Management for the Safe Operation of Ships: The International Safety Management code for ship proprietor and the operator is described clearly.
Chapter X – Safety measures for high-speed craft: security code for the high-speed craft is defined.
Chapter XI-1 & 2– Special measures to reinforce maritime security: Special and enhanced survey for secure operation, different operational necessities and ISPS code is briefed on this chapter.
Chapter XII – Additional security measures for bulk carriers: Includes security requirement for above 150 meters size bulk provider.
Chapter XIII – Verification of Compliance
Chapter XIV -Safety Measures for Ships Operating in Polar Waters
Let’s take every Solas chapter intimately:
SOLAS Chapter I
In the SOLAS Chapter 1; General Provisions, Surveys and certification of all the security objects, construction, equipment and so on. are included.
This chapter is additional subdivided into 3 parts- Part A, Part B and Part C.
Part A comprises 5 regulation which explains the “Application” of this chapter in various kinds of the ship together with the “Definition” of various terminology which is used within the chapter. The regulation might not be relevant to all forms of a ship; therefore a separate part of “Exceptions” and “Exemptions” can be supplied.
All the SOLAS chapters cowl a normal fundamental minimal criterion which applies to seagoing ships, no matter their location and nationality. It is feasible that the fabric or home equipment obtainable in a single nation are usually not obtainable for the ship overseas. An “Equivalent” Section can be supplied to take care of such a state of affairs.
Part B comprises the essential rules informing about surveys and certificates seagoing ships must need to be stated compliant with SOLAS. For this, 15 rules are stored beneath Part B. Regulation 6 to Regulation 11 offers particulars of various survey requirement on completely different ships, gear, equipment and so on. clauses on the right way to do the restore and what sort of surveys to undergo.
What is the Harmonised Survey System for Ships?
Regulation 12 to Regulation 18 explains the completely different requirement for certification obtained submit surveys.
Regulation 19 – Control: This regulation explains the jurisdiction of native authorities a overseas ship is voyaging, akin to coast guard, port state and so on. to examine the vessel for making certain the security of the ship. It additionally explains the step to be taken by the federal government authorities to inform the involved (subsequent port of name, proprietor, class and so on.) and the right way to train the management.
Regulation 20 – Privileges: this regulation explains if the ship can or can’t declare any privileges relying upon the certificates it holds.
Part C of Chapter 1 comprises just one regulation, i.e. Regulation 21, which explains how a contracting authorities can perform an inquiry for the ship which was concerned in an incident and causalities and what sort of info must be collected and to be handed by.
SOLAS Chapter II-1
Construction – Subdivision and stability, equipment and electrical installations: This chapter of SOLAS Deals with watertight integrity of the ship, together with the passenger’s vessel and contains of seven components, explaining the requirement for structural, equipment, electrical, stability and different standards for a secure ship.
Part A comprises 3 rules which clarify the “Application” of this chapter on ships as per their keel laying. The rules clarify the “Definition” of various terminology which is used within the chapter.
Part A-1 contains of rules explaining the requirement for the construction of the ship together with protecting coating, towing preparations, deck gear fittings, building and drawings and so on. It additionally contains the regulation on the right way to present entry to completely different components of oil tanker and bulk provider and the construction entry handbook which comprises the main points of the construction together with plans for technique of entry. Method to assemble a ship which complies with the regulation for cover in opposition to noise can be included.
Part B of this regulation explains the steadiness and watertight integrity requirement. Under Part B 1, the rules (Regulation 5 to eight) defines the required situations for sustaining the intact stability of the cargo ship and passenger ship. It additionally features a requirement on the knowledge which must be equipped to the grasp on the steadiness of the vessel explaining the right way to calculate the steadiness elements in several situations.
Part B 2 contains of 4 rules (Regulation 9 to 17) which takes care of the watertight integrity of the ship (each passenger and cargo ship) by enlisting the constructional and testing necessities of watertight and different essential bulkheads, and the availability of the double backside on ships apart from tanker ships.
Part B 3 explains the requirement for the subdivision load line project for passenger ships.
Part B 4 of this chapter contains of seven rules ( Regulation 19 to Regulation 25) for the requirement of stability administration explaining the inspections, preventions, harm management drills, and data for cargo and passenger ships.
Part C focuses on completely different equipment set up within the engine room together with the requirement of emergency installations within the passenger ships from regulation 26 to regulation 39.
Part D of this chapter (from regulation 40 to 45) focuses on {the electrical} set up requirement for cargo and passenger ships together with the emergency supply and preparations together with electrical security and hazards.
Part E clarifies the requirement for unattended equipment house beneath regulation 46 to 54 explicitly.
Part F of this chapter provides the main points concerning the different design and association for the ship’s equipment and electrical system beneath regulation 55. It additionally explains the storage and distribution requirement for the low flashpoint gasoline system.
Part G explains the applying and necessities as per the regulation 56 and 57 for the ships utilizing low flash level fuels.
SOLAS Chapter II-2
Fire safety, fireplace detection and fireplace extinction: This chapter elaborates the means and measure for fireplace safety in lodging, cargo areas and engine room for the passenger, cargo and tanker ship. This chapter is split into 7 components, explaining the varied requirement for fireplace security system put in on a ship.
Part A comprises rules 1 to three which explains the “Application” of this chapter on ships building date and the rules additionally explains the “Definition” of various terminology which is used within the chapter and the target and practical requirement of this chapter.
Part B of this chapter specifies the requirement to stop fireplace and explosion on cargo ship together with tankers. It has 3 rules from Regulation 4 to regulation 6; Regulation 4 giving the main points of the right way to forestall the ignition of a flamable supply current on ships together with the constraints and preparations on using gasoline and lube oils used onboard, and prevention of fireplace within the cargo areas of the tanker ship.
Regulation 5 laid down the requirement to curb the expansion of the hearth in several areas on the ship, which incorporates reducing anyone aspect of the hearth triangle, i.e. to regulate both air provide, oil provide or the warmth supply (utilizing safety supplies like insulation, linings and so on.) within the potential hazardous house.
Regulation 6 of this half concentrate on discount of hazards to human life from merchandise which launch smoke and poisonous gases (akin to paint, varnish and so on.).
Part C of this chapter contains of 5 rules (Regulation 7 to Regulation 11) and focuses on requirement to suppress the hearth on the earliest, together with detection and management of smoke and flames, containment necessities, structural integrity of the house to stop spreading of fireplace and firefighting methods and gear for use on ships equipment, lodging and cargo areas.
Part D focuses on the escape of the seafarers or passengers in case of fireplace or every other emergency. Regulation 13 explains the varied requirement for technique of escape for various kinds of ships (cargo ship, passenger ship, RoRo ship and so on.), gear and methods which helps in escaping from the hazardous place and so on.
Part E of chapter II-2 include Regulation 14 to regulation 16 offering info on the upkeep of the hearth detection, combating, and management gear on cargo ships together with tankers and passenger ships. It additionally explains the requirement for coaching and drills to be carried out on fireplace security onboard ship. Regulation 16 focuses on the hearth security booklet which ought to be stored on board ship for all sorts of vessel.
Part F of this chapter provides the main points concerning the different design and association for the ship’s fireplace security beneath regulation 17.
Part G comprises a particular requirement for the operations that are carried out on the tanker and bulk provider ships akin to helicopter operation (Regulation 18) giving particulars of various constructional, security and firefighting preparations. Regulation 19 offers security measures for carrying harmful items in a container, bulk, tanker or Roro ships.
Regulation 20 focuses on ships which carry automobile as cargoes together with passengers explaining prevention, detection, and containment of fireplace on such ships. Regulation 21, 22 and 23 are passenger-centric, describing the requirement a passenger ship ought to comply with in case of fireplace incident onboard ship to avoid wasting passenger and ship from a significant accident.
SOLAS Chapter III
Life-saving home equipment and preparations: All the lifesaving home equipment and there use in several conditions in response to the ship sort is described on this chapter.
This chapter contains of three Parts. Part A comprises 5 regulation which explains the “Application” of this chapter in various kinds of the ship together with the “Definition” of various terminology which is used within the chapter. The regulation might not be relevant to all forms of a ship; therefore a separate part of “Exceptions” and “Exemptions” can be supplied. Further, onboard testing and manufacturing testing procedures are additionally defined.
Part B contains of complete 32 rules (from Regulation no. 6 to 37) coping with the necessities of life-saving home equipment on passenger and cargo ships. Regulation 6 describes the communication equipment (Radio, Pyrotechnics and so on.) used for security and life-saving conditions on vessels.
Regulation 7 checklist downs the requirement for the non-public life-saving equipment akin to lifejackets, lifebuoys, immersion swimsuit and so on.
Regulation 8 to Regulation 11 comprises the instruction on muster station, survival craft operation and manning, together with their embarkation preparations explaining the completely different necessities.
Regulation 12 particularly tackle the placement of survival craft in a cargo ship (apart from free fall lifeboat). Regulation 13 to Regulation 17 particulars on the stowage and mandatory association required for the lifeboat, liferaft, marine evacuation system, restoration boat on the ship and Man Overboard Operation.
Regulation 18 lists down the requirement for line throwing home equipment used on the ship. Regulation 19 offers with varied coaching and drills requirement for onboard crew.
Regulation 20 utilized to all of the ships for operational readiness, upkeep and survey requirement of survival crafts and different lifesaving home equipment onboard ship.
Regulation 21 to Regulation 30 inform concerning the further requirement for passenger ship about survival crafts and all lifesaving home equipment on the passenger ships, together with drills for passengers onboard ship and helicopter operation in a passenger ship (ro-ro passenger ships of 130m in size ought to be supplied with a helicopter touchdown space).
Regulation 31 to Regulation 34 inform concerning the further requirement for cargo ship about survival crafts and all lifesaving home equipment on the ships.
Regulation 35 to 37 comprises varied directions for onboard upkeep, muster lists and so on. and availability of coaching handbook and different onboard coaching aids on the ship.
Part C of this chapter provides the main points concerning the different design and association for ship’s lifesaving home equipment beneath regulation 38.
SOLAS Chapter IV
Radio communications: This chapter Includes necessities of various radio communication gear used onboard ships akin to GMDSS, SART, EPIRB and so on for cargo and passenger vessel. This chapter is split into 3 components; Part A, Part B and Part C.
Part A comprises rules 1 to 4 which explains the “Application” of this chapter and the rules additionally explains the “Definition” of various terminology which is used within the chapter and the target and practical requirement of this chapter. Further, it contains the exemptional requirement and the main points of GMDSS satellite tv for pc suppliers.
Part B consisted of Regulation 5 explaining the provisions of radiocommunication companies and the identities of GMDSS by the contracting authorities.
Part C insists on the ship-based requirement for the radio gear and contains of 13 rules. Regulation 6 provides the main points of radio set up requirement on all forms of ship. Regulation 7 offers particulars of various radio gear minimal requirement that are for use on ships.
Regulation 8 to Regulation 11 offers the main points of radio set up functionality to preliminary ship to shore communications and alerts in Sea areas A1, A2, A3 and A4.
Regulation 12 lists down the extra duties of the officer on radio communication gear throughout a watch.
Regulation 13 provides the main points of the vitality supply for all of the radio communication gear together with emergency reserve supply of energy and battery energy.
Regulation 14 and 15 provides the main points of efficiency requirements and upkeep required to be carried out on radiocommunication gear.
Regulation 16, 17 and 18 present the necessity for radio personnel qualification and completely different data and logs which must be up to date within the ship log system.
SOLAS Chapter V
Safety of navigation: This chapter consists of complete 35 rules coping with all of the seagoing vessels of all sizes, from boats to VLCCs, and contains passage planning, navigation, misery sign and so on.
Regulations 1 to three explains the “Application” of this chapter on the security of navigation and the rules additionally explains the “Definition” of various terminology which is used within the chapter and the target and practical requirement of this chapter. Further, it contains the exemptional requirement to be granted by the administration to a complying ship.
Regulation 4 and 5 lists down completely different navigational and mineralogical service warnings that are important for a navigating officer for secure passage plan.
Regulation 6, 7,8 and 9 focuses on companies such because the ice patrol service for secure navigation in North Atlantic, search and rescue companies (when receiving misery alert from the ship), utilization of life-saving alerts and hydrographic companies (for the compilation of hydrographic knowledge and publication) by the contracting authorities.
Regulation 10 comprises the main points for the requirement of ships’ routeing system for secure and environment friendly navigation.
Regulation 11 lists down the necessity of reporting system to contribute in direction of maritime and environmental security, the place the seagoing ship experiences to the involved authorised physique.
Regulation 12 offers the requirement for Vessel Traffic Service (VTS) undertaken by the contracting authorities for secure navigation within the coastal space, channel, port neighborhood and space of maritime site visitors.
Regulation 13 defines the function of the contracting authorities for an association of multinational and operation of aids to navigation.
Regulation 14 lists down the minimal manning requirement and crew efficiency for a seagoing ship
Regulation 15 provides particulars of bridge design and procedures together with the association of navigation methods and gear.
Regulation 16 and Regulation 17 offers the necessity for upkeep of navigation gear and their electromagnetic compatibility.
Regulation 18 provides the phrases for surveys, approval standards and efficiency customary of navigational gear and system together with VDR.
Regulation 19 offers the requirement for carrying a navigational system and gear onboard ship as per the date of building and likewise as per the capability of the vessel in gross tonnage. It additionally explains the requirement for Long Range Identification and Tracking of Ships.
Regulation 20 explains the requirement for Voyage Data Recorder on ships for aiding in causality investigations.
Regulation 21 offers the main points of the International Code of Signals which a radio set up on a ship ought to carry.
Regulation 22 talks concerning the visibility requirement from the ships’ bridge window and Regulation 23 explains the pilot switch association.
Regulation 24 explains using heading and monitor management system when the ship is in restricted visibility or excessive site visitors space.
Regulation 25 and 26 lists down the regulatory requirement for {the electrical} energy supply, testing, and drills for steering gear methods.
Regulation 27 talks concerning the nautical charts and publication obtainable onboard ship for passage and voyage.
Regulation 28 offers the main points of data to be stored for all of the navigational actions by ship’s navigation officer.
Regulation 29 insist on the requirement for the ship’s officer to grasp completely different life-saving alerts utilized in misery. Regulation 30 lists the operational limitations of passenger ships concerning secure navigation.
Regulation 31, 32, 33 and 34 comprise a requirement for the grasp of the ship on the right way to act in a harmful state of affairs by sending hazard message (whereas encountering any harmful navigation state of affairs to the contracting authorities utilizing a message or International code of Signal. It additionally contains the kind of info which must be despatched to the authorities.
Further, the regulation additionally explains the obligations/ procedures on offering help to the ship in peril and the right way to keep away from such a state of affairs which may turn out to be a hazard. Regulation 35 strictly prohibits using misery sign for every other objective apart from explains within the above rules.
SOLAS Chapter VI
Carriage of Cargoes and Oil Fuel: This chapter defines storage and securing of various kinds of cargo and containers, however doesn’t embrace oil and fuel cargo. This chapter is additional divided into 3 components; Part A, Part B, and Part C.
Part A comprises rules 1 to Regulation 5. Regulation 1 explains the “Application” of this chapter and likewise explains the “Definition” of various terminology which is used within the chapter and the necessities to hold the strong cargo apart from grain.
Regulation 2 tells concerning the info change to be achieved between the shipper and the grasp on the kind of cargo being loaded.
Regulation 3 explains the necessity for Oxygen analyzer and different fuel detection gear for monitoring of these strong cargoes which emits poisonous or flammable gases.
Regulation 4 describes the main points of utilizing pesticides on ship achieved for fumigation objective.
Regulation 5 offers the knowledge on stowing and securing of the cargo. It additionally lists down the requirement of MSDS for oil gasoline carried on board ship. Further, it explains the requirement to ban the blending of bulk liquid cargo and manufacturing course of throughout sea voyages.
Part B of this chapter checklist down the particular provision for carrying strong bulk cargoes and it include Regulation 6 and seven which explains the process to simply accept a cargo and the right way to load, unload the stow such cargo.
Part C focuses on the requirement for carriage of grains beneath Regulation 8 and 9 which offers the definitions of International Grain Code and different important phrases associated to grains ailing with the standards to hold grain cargoes on the ship.
Solas Chapter VII
Carriage of harmful items: Defines the International Maritime Goods Code for storage and transportation of harmful items. This chapter is additional divided into 4 components; Part A, Part B, Part C and Part D.
Part A is supplied with info on the carriage of harmful items within the packaged type beneath 7 rules. Regulation 1, 2 and three clarify the “Application” of this chapter and likewise explains the “Definition” of various terminology which is used within the chapter together with the necessities to hold harmful items within the packaged type.
Regulation 7 is devoted for Carriage of harmful items in a strong bulk type defining the phrases used beneath this regulation together with the applying of the phrases. It additional explains the documentation and stowage with segregation requirement for such sort of cargoes. The reporting of the incident and different situation associated to the damaging items carried in strong bulk type can be supplied.
Part B of this chapter explains the main points about building and gear for carrying harmful liquid chemical in bulk. Regulation 8, 9 and 10 clarify the Definition” of various terminology which is used within the chapter and “Application” of this chapter together with the necessities for chemical tankers which carry such cargoes.
Part C of this chapter explains the main points about building and gear for carrying liquified fuel in bulk as cargo. Regulation 11, 12 and 113 tells the Definitions of various terminology that are used within the chapter and “Application” of fuel ships together with the necessities for fuel tankers which carry such cargoes.
SOLAS Chapter VIII
Nuclear ships: The code of security for the nuclear-propelled ship is said on this chapter.
This chapter consists of 12 rules explaining the applying, exemptions, approvals, and requirement (for reactor installations), Safety in opposition to radiation, security evaluation, working handbook, surveys and certifications, Controlling authority and steps in case of any causality resulting from radiation and so on.
SOLAS Chapter IX
Management for the Safe Operation of Ships
The International Safety Management code for ship proprietor and the operator is described clearly. Regulation 1 and a pair of of this chapter explains the main points concerning the “Application” of SOLAS Chapter 9 and likewise explains the “Definition” of various terminology which is used within the chapter.
Regulation 3 offers the requirement to adjust to the ISM code adopted by essential certifications in Regulation 4, which incorporates DOC, SMC and so on.
Regulation 5 and Regulation 6 checklist down the upkeep of situations and verification & management respectively.
SOLAS Chapter X
Safety measures for high-speed craft
This chapter is devoted to high-speed crafts solely, explaining the security necessities and contains of three rules decoding the Definitions of various terminology that are used within the chapter and “Application” of high-speed craft together with the necessities for high-speed crafts.
SOLAS Chapter XI
This chapter is split into two sections.
Section one, i.e. Chapter XI -1 take care of the Special measures to reinforce maritime security which incorporates Special and Enhanced survey for secure operation. The second part of this SOLAS chapter which is Chapter XI-2 checklist down the rules for particular guidelines to enhance maritime safety.
Chapter XI-1 consist of seven rules. Regulation 1 offers details about the authorization of a recognised organisation. Regulation 2 compiles the necessities for the improved survey for bulk carriers and oil tankers together with the harmonization of survey intervals of ships which aren’t subjected to the ESP code.
Regulation 3 offers the main points of the ship identification quantity and firm cum proprietor identification quantity.
Regulation 4 explains the function of Port state management on operational necessities.
Regulation 5 offers with the continual synopsis report which is supplied onboard as a historic overview of the ship info.
Regulation 6 specifies the extra requirement for the investigation of marine causality and incidents.
Regulation 7 tells concerning the requirement for ambiance testing instrument for enclosed areas for measuring oxygen, flammable gases, H2S, Carbon mono oxide and so on.
Chapter XI-2 offers with maritime safety measures which all of the events concerned in a maritime commerce must comply with; i.e. ship, port, ship proprietor, contracting authorities and authorities. This SOLAS chapter consists of 13 rules, and Regulation 1 and a pair of clarify the Definition” of various terminology which is used within the chapter and the main points concerning the “Application” of this chapter.
Regulation 3 focuses on the contracting authorities stating their obligation in direction of maritime safety.
Regulation 4 lists down the requirement for firms and ships on the right way to adjust to the ISPS code adopted by Regulation 5 which offers with the precise duty of the businesses in direction of maritime safety.
Regulation 6 specifies the very important requirement for all seagoing ship concerning the Ship Security Alert System (SSAS).
Regulation 7 offers with the threats to the vessels which must be set as a safety stage by the contracting governments.
Regulation 8 lists down the discretion for the grasp for taking account of ship security and safety.
Regulation 9 explains concerning the compliance and management measures {that a} ship ought to exhibit in port and regulation 10 states the related necessities for port services beneath ISPS code.
Regulation 11 and 12 talks concerning the different and equal safety association by the contracting authorities and administration.
Regulation 13 offers with the completely different info that must be communicated to the ship and ship supervisor.
SOLAS Chapter XII
Additional security measures for bulk carriers: This chapter Includes security requirement for above 150 meters size bulk provider. It consists of 14 rules.
Regulation 1,2 and three provides particulars concerning the “Definition” of various terminology that are used within the chapter and the main points concerning the “Application” of this chapter, adopted by the implementation schedule for the survey as per the date of building.
Regulation 4 The harm stability necessities for bulk carriers are defined on this regulation.
Regulation 5 & 6 offers the main points of structural power and different structural necessities for bulk provider ship.
Regulation 7 offers with the surveys and upkeep necessities of the majority carriers adopted by Regulation 8 which explains the knowledge on compliance for bulk carriers.
Regulation 9 focuses on these bulk provider ships that are unable to adjust to regulation 4 due to the designing of cargo holds. Regulation 10 lists down the requirement for declaring the strong bulk cargo density.
Regulation 11 offers particulars concerning the loading devices used for cargo loading on bulk provider ships.
Regulation 12 lists down the phrases for having water ingress alarm in holds, ballast house and different dry areas in a bulk provider ship.
Regulation 13 applies to all the majority carriers no matter their date of building and explains the need of pumping methods to empty the ballast tanks.
Regulation 14 focuses on the restrictions in direction of the majority provider ships from crusing with an empty cargo maintain.
Apart from the above SOLAS 12 Chapters, the under two are thought of to be SOLAS new chapters which have been added in recent times.
SOLAS Chapter XIII
Verification of Compliance: This chapter was adopted on 22 May 2014 which requires all of the Contracting Party to bear periodic audits by the authorised group following the audit customary to confirm compliance with and implementation of the current Convention.
This chapter consists of regulation 1 to regulation 3 explaining the “Definition” of various terminologies that are used within the chapter and the main points concerning the “Application” of this chapter, adopted by the verification system for contracting authorities.
SOLAS Chapter XIV
Safety Measures for Ships Operating in Polar Waters – As the title recommend, the SOLAS chapter 14 offers with the ships that intend to function throughout the Arctic and Antarctic areas and wish to hold Polar Ship Certificate.
This Code entered into pressure on 1 January 2017 and explains the shipowners and ship managers concerning the steps to be taken to have their ships in compliance throughout the completely different classes. This is likely one of the newest chapter launched inside SOLAS in 2017.
It contains of 4 Regulations ranging from regulation 1 & 2 which supplies the main points concerning the definitions of the terminology used on this chapter and utility of this code.
Regulation 3 explains the necessities for ships to which this chapter applies adopted by regulation 4 which recommend the phrases for different design and association for vessels crusing in Arctic and Antarctic areas.
MARPOL 73/78
Just like SOLAS, which regulates the delivery trade to comply with minimal requirements to safeguard life at sea. MARPOL is one other essential conference which safeguards the marine surroundings in opposition to ship air pollution. MAPOL and SOLAS are thought of to be two efficient security and environmental safety instruments of IMO.
MARPOL 73/78, because it got here into pressure in 1973 and later revised by the protocol in 1978, ensures that delivery stays the least environmentally damaging modes of transport. It clearly highlights the factors to make sure that the marine surroundings is preserved by the elimination of air pollution by all dangerous substance which could be discharged from the ship.
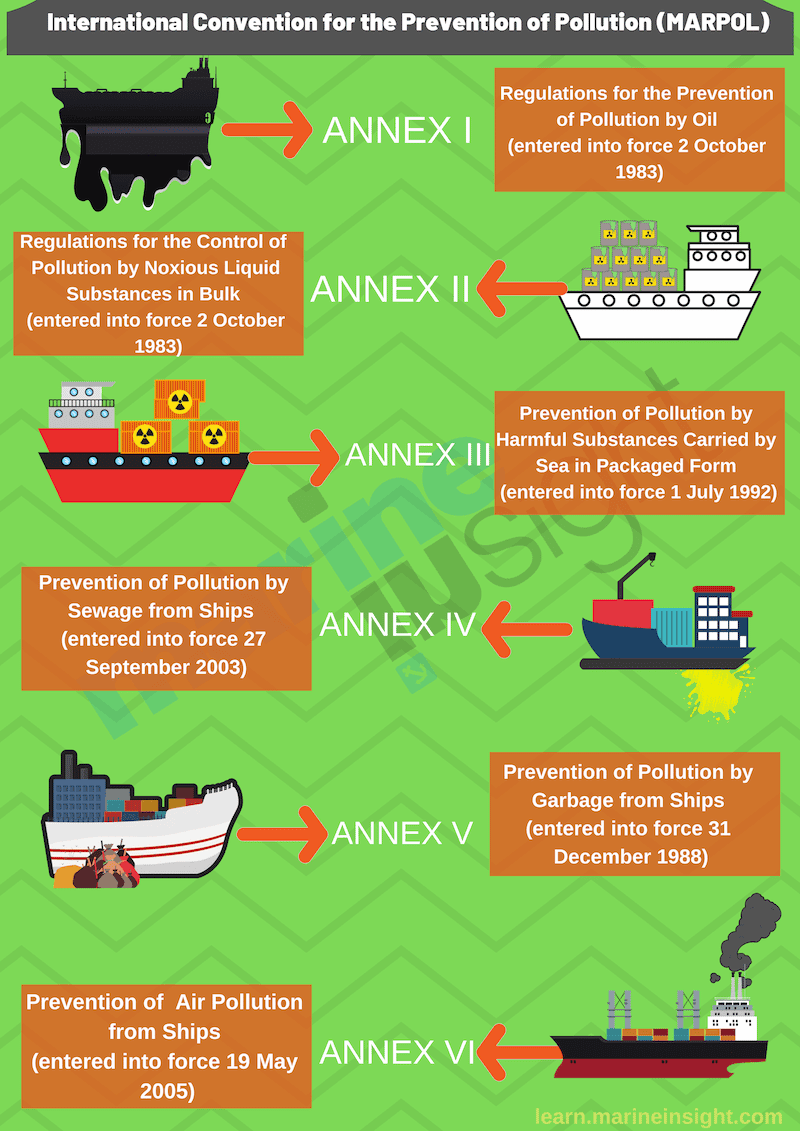
This marine environmental conference consists of six carried out annexes for controlling and eliminating of marine air pollution.
They are as follows:
Annex I: Regulation for prevention of air pollution by oil (October 1983).
Annex II: Regulations for management of air pollution by Noxious Liquid Substance in bulk (April 1987).
Annex III: Regulation for prevention of air pollution by dangerous substance carried at sea in packaged type (July 1992).
Annex IV: Regulation for prevention of air pollution by sewage from ships (Sep 2003).
Annex V: Regulation for prevention of air pollution by Garbage from ships (Dec 1998).
Annex VI: Regulation for prevention of Air air pollution from ships (May 2005).
They are as follows:
MARPOL Annex I
Regulation for the prevention of air pollution by oil (October 1983).
This regulation was adopted on 2nd October 1983 to regulate and forestall any oil discharge from ship deliberately or by accident. It contains of 11 chapters which collectively comprises 47 Regulations.
Chapter 1 provides a normal description about MARPOL ANNEX I and consists of 5 rules which clarify the “Application” of this chapter in various kinds of the ship together with the “Definition” of various terminologies that are used within the chapter. The regulation could not apply to all forms of ship therefore a separate part of “Exceptions” and “Exemptions” can be supplied. It additionally explains the situation the place an administrator could enable different fittings, supplies, home equipment and so on. to be put in on ships to fulfil this annex.
Chapter 2 offers with Surveys and Certifications requirement for all oil tanker ships of 150GT and different sips of 400 GT. And contains of 5 rules.
Regulation 6 describes the requirement for various surveys to adjust to MARPOL annex 1.
Regulation 7 offers the phrases to challenge or endorse the IOPP certificates to the ship submit profitable survey by the suitable administration. Regulation 8 additionally describes the right way to challenge or endorse the certificates by one other contracting authorities, adopted by Regulation 9 which inform the type of the certificates together with languages akin to English or official language of issuing nation.
Regulation 10 explains the length and validity of certificates and supply timelines for renewal of certificates.
Regulation 11 phrases the authority of port state management beneath Annex 1 to examine the ship for compliance.
Chapter 3 offers with the Requirements for Machinery areas for all ships and checklist down the necessities beneath Regulation 12 to 17, in order that the engine room and different equipment areas are compliant with the MARPOL Annex 1.
Regulation 12 explains the requirement of storage tanks for oil residues produced on all forms of the ship resulting from equipment operation and methodology to eliminate the oil residue. It additional offers particulars to guard the gasoline oil tanks for ships having gasoline oil capability 600m3 and above.
Regulation 13 describes the requirement for traditional discharge connection on a ship to eliminate oil residue from sludge and bilge tanks.
Regulation 14 The necessities of oil filtration gear onboard ship for discharging engine room bilges or ballast water from gasoline oil tanks is given on this regulation, adopted by Regulation 15 which restricts the discharge of handled bilges in particular areas.
Regulation 16 explains the requirement of segregating oil and water ballast which is carried within the gasoline tank of the ship.
Regulation 17 lists down the necessity for a compliant oil report e-book for equipment house in oil tankers of 150GT and above and different ships of 400 GT and above.
Chapter 4. offers with the Requirements of Cargo areas in an oil tanker ship itemizing down varied regulation (Regulation 18 to 36).
Chapter 5 describes the right way to forestall air pollution which may come up from an oil air pollution incident. Regulation 37 which checklist the SOPEP or Shipboard Oil Pollution Emergency plan offers the main points.
Chapter 6 lists the requirement for the reception services to which the ship will eliminate the oily bilge/ sludge to beneath Regulation 38 offering particulars of the power inside and outside particular areas.
Chapter 7 offers the particular requirement for mounted or floating platform to adjust to Annex 1 of MARPOL with Regulation 39.
Chapter 8 offers with the prevention of air pollution which can occur throughout cargo oil in between tankers at sea often known as Ship to Ship Transfer (STS). It contains of three regulation from 40 to 42.
Regulation 40 offers the scope of utility for this chapter and Regulation 41 lists down the foundations on security and environmental safety in the course of the STS operation, adopted by Regulation 42 which tells the notifications which have to be supplied by the ship to port state and all the opposite events concerned within the operation.
Chapter 9 carries the main points for the particular requirement for using carriage of oils within the Antarctica space with Regulation 43.
Chapter 10 offers with the Verification of compliance with the availability of this conference beneath Regulation 44 and 45, offering particulars of the applying and the method for verification of compliance.
Chapter 11 checklist down the essential requirement on worldwide code for ships working in Polar waters beneath Regulation 46 and 47. Regulation 46 lists down the definition for this annexe adopted by Regulation 47 for utility and requirement for the ships crusing in polar waters.
MARPOL Annex II
Regulations for the management of air pollution by Noxious Liquid Substance in bulk (April 1987).
This Annex was adopted on sixth of April 1987 which offers with the management and forestall air pollution because of the noxious liquid substance in bulk, deliberately or by accident. It contains of 10 chapters which collectively comprises 22 Regulations.
Chapter 1 provides normal particulars on MARPOL ANNEX II and consists of 5 rules offering the “Definition” of various terminologies that are used within the chapter and explains the “Application” of this chapter in various kinds of ship (Chemical tankers and so on.). The regulation might not be relevant to all forms of a ship; therefore a separate part of “Exceptions” and “Exemptions” can be supplied. It additionally explains the situation the place an administrator could enable different fittings, supplies, home equipment and so on. to be put in on ships to satisfy this annex.
Chapter 2 offers the main points of various classes of Noxious liquid substance beneath regulation 6.
Chapter 3 checklist down the necessity for surveys and certification with 4 rules from regulation 7 to 10. Regulation 7 offers with the surveys and certifications wanted by chemical tanker following the availability of the International Bulk Chemical code.
Regulation 8 particulars the necessity for various surveys for the ships carrying noxious liquid substances in bulk adopted by issuing and endorsing of the certificates beneath Regulation 9. The length and validity of the certificates are supplied in Regulation 10.
Chapter 4 specifies the Design, Construction, association, and gear for ships carrying Noxious cargo in bulk beneath regulation 11, adopted by Regulation 12 which offers the main points of pumping, piping, unloading association and slop tanks.
Chapter 5 carries 3 regulation from 13 to fifteen for offering the main points of operational discharge of residues of noxious liquid substances. Regulation 13 lists the necessity for management of discharges of Noxious liquid substance residues.
Regulation 14 and 15 present the main points of Procedure and association handbook and Cargo report e-book which must be stuffed by the ships’ officers.
Chapter 6 which include Regulation 16 describe the function of presidency and authorised events akin to port state management on measures of management to examine, survey and assess the ships to hold the cargo beneath MARPOL Annex II.
Chapter 7 offers with Prevention of Pollution arising from an incident involving noxious liquid substance and include Regulation 17 giving the main points of Shipboard air pollution emergency plan for noxious liquid substances.
Chapter 8 lists the requirement for the reception services to which the ship can eliminate the residues and combination generated from noxious liquid substances beneath Regulation 38 offering particulars of the power and terminal unloading preparations.
Chapter 9 offers with the Verification of compliance with the availability of this conference beneath Regulation 19 and 20, offering particulars of the applying and the method for verification of compliance.
Chapter 10 checklist down the essential requirement on worldwide code for ships working in Polar waters beneath Regulation 21 and 22. Regulation 21 lists down the definition for this annex adopted by Regulation 22 for utility and requirement for the ships crusing in polar waters.
MARPOL Annex III
Regulation for prevention of air pollution by dangerous substance carried at sea in packaged type (July 1992).
This Annex offers with these substances that are hazardous in nature and carried in packaged cargo. The identification of such materials is supplied within the IMDG Code. The MARPOL Annex III got here into pressure on 1 July 1992 and comprised of two Chapters containing 11 rules.
Chapter 1 provides a normal particulars on MARPOL ANNEX III and include 9 rules.
Regulations 1 & 2 explains the “Definition” of various terminologies that are used within the chapter and the “Application” of this chapter in various kinds of ships that are carrying Hazardous items.
Regulation 3 & 4 lists down the requirement of packaging and Marking/labelling of the packages carrying IMDG cargoes.
Regulation 5 offers the main points of the documentation that are wanted by the ship which is carrying hazardous materials beneath MARPOL Annex 3
The storage requirement and amount limitations for carrying dangerous substances in bulk are supplied beneath Regulation 6 & 7.
Regulation 8 lists down the exceptions which a ship carrying dangerous cargo in bulk can have beneath varied circumstances.
The authorisation of port-state management on the operational requirement of ships carrying such substance beneath MARPOL Annex III is listed in Regulation 9.
Chapter 2 offers with the Verification of compliance with the availability of this conference offering particulars of the applying and the method for verification of compliance beneath Regulation 10 and 11.
MARPOL Annex IV
Regulation for the prevention of air pollution by sewage from ships (Sep 2003).
Entered into pressure on 27 September 2003, this Annex focuses on prevention of sewage air pollution from ships. It has 7 Chapters comprising of 18 Regulations.
Chapter 1 provides a normal description about MARPOL ANNEX IV and consist of three rules which explains the “Definition” of various terminologies that are used within the chapter and “Application” of this chapter in various kinds of ships. The regulation might not be relevant to all forms of ship therefore a separate part of “Exceptions” can be supplied.
Chapter 2 checklist down the necessity for surveys and certification with 5 rules from regulation 4 to eight. Regulation 4 offers with the surveys to be achieved on ships implicated by this Annex. Regulation 4 & 5 present the main points for challenge or endorsement of certificates by the administration and by one other authorities. Regulation 7 & 8 provides particulars of type, length, and validity of the sewage air pollution prevention certificates.
Chapter 3 offers the necessity of getting Equipment and management of sewage discharge from the ship. Regulation 9 beneath this chapter offers particulars of sewage system requirement on ships adopted by Regulation 10 and 11 for having a regular sewage discharge connection to switch sewage to port services and discharge of sewage at sea inside and out of doors particular areas.
Chapter 4 consist of two rules (12 & 13) with the main points of the reception services requirement. Regulation 12 offers the main points to the federal government companies concerning the compliance to have a reception facility and Regulation 13 lists down the requirement of reception services for Passenger ships in particular areas.
Chapter 5 which include Regulation 14 describe the function of presidency and authorised events akin to port state management on measures of management to examine, survey and assess the ships beneath MARPOL Annex IV.
Chapter 6 offers with the Verification of compliance with the availability of this conference offering particulars of the applying and the method for verification of compliance beneath Regulation 15 and 16.
Chapter 7 checklist down the essential requirement on worldwide code for ships working in Polar waters beneath Regulation 17 and 18. Regulation 17 lists down the definition for this annex adopted by Regulation 18 for utility and requirement for the ships crusing in polar waters.
MARPOL Annex V
Regulation for the prevention of air pollution by Garbage from ships (Dec 1998).
This annexe offers with the rubbish produced onboard ships and methods to stop air pollution from the identical. It was enforced on 31 December 1988, having 3 Chapters with 14 Regulations.
Chapter 1 provides normal particulars on MARPOL ANNEX II and consists of 10 rules offering the “Definition” of various terminologies that are used within the chapter beneath Regulation 1 and explains the “Application” of this chapter in various kinds of ship Regulation 2.
Regulation 3 lists down the main points of the overall prohibition on the discharge of rubbish at sea adopted by Regulation 4 for the discharge of rubbish outdoors particular areas.
Regulation 5 specifies the particular necessities for the discharge of rubbish from mounted and floating platforms. The requirement for discharge of rubbish within the particular space is given beneath Regulation 6.
Regulation 7 & 8 describes the receptions services exception and necessities together with those that are contained in the particular areas.
Regulation 9 consist function of port-state management on measures of management to examine, survey and assess the ships beneath MARPOL Annex V.
Regulation 10 offers with the necessity for Garbage Management Plan (GMP) together with report books and placards.
Chapter 2 offers with the Verification of compliance with the availability of this conference beneath Regulation 11 and 12
Chapter 3 checklist down the essential requirement on worldwide code for ships working in Polar waters beneath Regulation 13 and 14. Regulation 13 lists down the definition for the aim of this annex adopted by Regulation 14 for utility and requirement for the ships crusing in polar waters.
MARPOL Annex VI
Regulation for prevention of Air air pollution from ships (May 2005).
This MARPOL Annex offers explicitly with methods to stop air pollutions from ships. It got here into pressure on nineteenth May 2005 having 5 chapters with 25 Regulations.
Chapter 1 provides a normal description about MARPOL ANNEX VI and consists of 4 rules which clarify the “Application” of this chapter in various kinds of the ship together with the “Definition” of various terminologies that are used within the chapter. The regulation could not apply to all forms of ship therefore a separate part of “Exceptions” and “Exemptions” can be supplied. It additionally explains the situation the place an administrator could enable different fittings, supplies, home equipment and so on. to be put in on ships to fulfil this annex.
Chapter 2 lists the survey, certification, and technique of management coping with air air pollution from the ship. It has 7 Regulation with Regulation 5 explaining the necessity of various surveys for the vessel having the association to stop air air pollution adopted by issuing and endorsing of International Air Pollution Prevention (IOPP) certificates and International Energy Efficiency Certificates (IEEC) in Regulation 6.
Regulation 7 offers the main points for challenge or endorsement of certificates by one other social gathering adopted by the types of certificates and assertion of compliance associated to gasoline oil consumption reporting in Regulations 8 for each IOPP and IEEC. The particulars for the validity of those certificates are supplied in Regulation 9.
Regulation 10 phrases the authority of port state management beneath Annex VI to examine the ship for compliance.
Regulation 11 explains how the administration and authorised social gathering can detect ships for the violation and the right way to implement this annexe.
Chapter 3 offers with the necessities for management of emissions from ships and consist of seven Regulations, beginning with the main points of ozone-depleting substances in Regulation12 akin to within the refrigerant used on ships.
Regulation 13 provides a short about Nitrogen Oxides (NOx) with completely different Tiers (Tier I, II and III) in and out of doors the emission management areas.
Regulation 14 provides a short about Sulphur Oxides (SOx) with the requirement for the amount of sulphur within the gasoline oil as per the yr, in and out of doors emission managed areas.
The emissions of Volatile Organic Compound from the oil tankers are taken under consideration in Regulation 15 offering the main points to adjust to the necessities.
Regulation 16 talks concerning the shipboard incineration operations and when the incineration is allowed.
Regulation 17 describes the receptions services necessities for disposing of ozone-depleting substance, residue from exhaust cleansing and so on.
To adjust to the exhaust emission necessities, correct gasoline oil is made obtainable to burn on ships, whose situation is described in Regulation 18.
Chapter 4 offers the Regulation on Energy Efficiency on Ships having Regulations 19 to 23. Regulation 19 talks concerning the utility of this chapter on ships of 400GT and above.
Regulation 20 and 21 present the main points of Attained Energy Efficiency Design Index (Attained EEDI) and Required EEDI.
The Ship Energy Efficiency Management Plan (SEEMP) necessities, which ought to be stored onboard, is supplied in Regulation 22. Further, the requirement for gasoline oil consumption knowledge assortment and reporting to the administration can be listed on this regulation.
Regulation 23 talks concerning the technical cooperation between completely different events (Administration, Government company, Shipping firm and so on.) to enhance the vitality effectivity of ships.
Chapter 5 offers with the Verification of compliance with the availability of this conference beneath Regulation 24 and 25.
Thus, SOLAS and MARPOL conventions stand as two strong pillars that assist the maritime trade by defending an important points – marine air pollution prevention and security of human life.
Disclaimer: The authors’ views expressed on this article don’t essentially mirror the views of Marine-Salvage. Data and charts, if used, within the article have been sourced from obtainable info and haven’t been authenticated by any statutory authority. The creator and Marine-Salvage don’t declare it to be correct nor settle for any duty for a similar. The views represent solely the opinions and don’t represent any pointers or advice on any plan of action to be adopted by the reader.
The article or photos can’t be reproduced, copied, shared or utilized in any type with out the permission of the creator and Marine-Salvage.















